UGT Run-Off Measuring System
The UGT Run-Off Measuring System is a modular field instrument designed to record, quantify and sample surface run-off and associated erosion loads from soil plots under natural conditions.
The system captures run-off water via a collecting gutter and directing channel system, routes the run-off through tipping counters and an auto-sampler, and collects water samples in ready bottles for further laboratory analysis.
It is designed to avoid blockages, back-water effects or flow rate reduction by eliminating bottlenecks in the flow path so that the erosion materials and waters move through unobstructed.
By combining this system with meteorological and soil hydrology sensors, you can obtain a comprehensive view of surface run-off, erosion processes, and plot‐scale water balance.
Key Feature /Highlights
- • Fully automated sampling of surface run-off: Up to 24 sample bottles (2 × 12) in autosampler magazine.
- • Dynamic sampling adapted to discharge intensity: at low flows the system fills all run-off, at high flows samples at intervals to distribute sample collection over the event.
- • Modular layout: collecting gutter, plot-limitation frames (e.g., 3 m × 10 m area), divider system, hoses and bypass tipping counters.
- • No bottlenecks: design ensures erosion material is transported unhindered; large debris filtered by stainless-steel sieve plate; minimal flow disturbance.
- • Low energy operation: free flow due to height difference, no pump required in the main run-off path; optional battery/solar support.
- • Robust materials: stainless steel or light metal housing; designed for outdoor field conditions including soil/erosion environments.
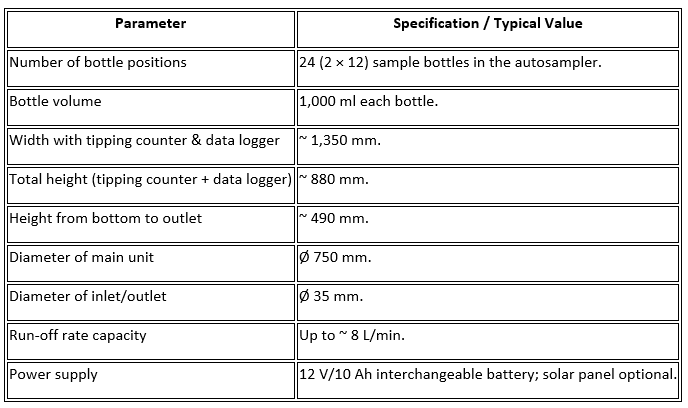
Technical Specification
Applications /Usage Areas
- • Field studies of surface run-off and soil erosion: capturing water and sediment load from defined plot areas under rainfall events.
- • Hydrology and watershed research: small catchment or slope hydrology where run-off quantification is essential.
- • Agricultural R&D: test effect of management practices (slope, vegetation cover, tillage) on run-off/erosion dynamics.
- • Environmental monitoring: measuring run-off from land-use change, construction sites, compacted soils, sealed surfaces.
- • Integrated water balance investigations: coupling run-off data with soil moisture, infiltration, meteorology and evapotranspiration systems.
Benefits /User Advantages
- • Automated sampling reduces manual intervention and ensures temporal resolution of run-off events.
- • Adaptation to discharge intensity means better sample distribution over the event, improving representativeness.
- • Modular and robust design means the system can be deployed in challenging field conditions with less maintenance.
- • Enables quantification of both the volume of run-off and the transported load (erosion material/sediment) when paired with appropriate analysis.
- • Provides reliable data that supports research, design (e.g., erosion control measures), and monitoring programmes.
Best Practice & Considerations
- • Ensure the plot limitation and collecting gutter are installed with proper slope and anchoring so that surface run-off is directed correctly into the system and bypasses are avoided.
- • Keep the inlet/collecting gutter free of large debris and maintain the stainless steel sieve to prevent blockage and maintain the designed flow path.
- • Calibrate and program the autosampler and tipping counters beforehand, set the sampling logic (low flow vs high flow) appropriately to your site’s expected run-off behaviour.
- • Check battery/solar power supply and data logger integrity regularly, especially in remote or long-term deployments.
- • Monitor and log site conditions (rainfall, soil moisture, antecedent conditions) to interpret run-off data in context.
- • Note that the quoted run-off rate capacity (~8 L/min) may limit use in extremely high intensity events; site design should account for maximum expected flow.
- • For accurate sediment/erosion load calculations, use compatible sampling bottles and pre-analysis methods to align with your sample size and lab protocol.
- • Ensure you understand the drainage and bypass path in the system: when tipping counter overflow occurs, bypass counter records excess—this ensures the full volume is quantified.
- • Prior to any rainfall event, inspect system for any puddling or unintended blockage that might cause back‐water, distortion of flow, or under-estimation.

