TDT Soil Moisture Sensor
This sensor uses the advanced Time Domain Transmission (TDT) technology to measure volumetric water content (VWC) of soil with high accuracy across different soil types and conditions. The digital version (SDI 12 compatible) provides robust performance even under varying soil conductivity, temperature, and salinity.
It is suitable for precision irrigation management, soil moisture monitoring in agriculture, hydrology, environmental research and long term installations.
Key Features / Highlights:
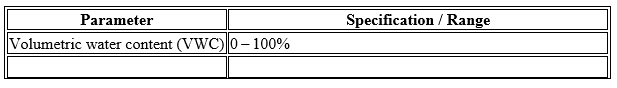
- • Measurement range: 0 100% volumetric water content.
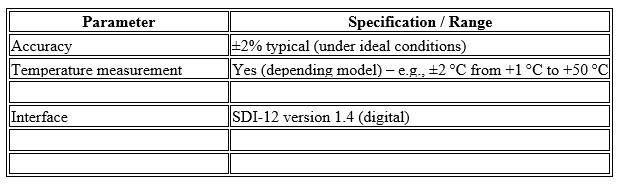
- • Typical accuracy ±2% VWC (in standard conditions) for the Digital TDT sensor.
- • SDI 12 (v1.4) digital output, allowing easy integration with data loggers and monitoring systems.
- • Works in all soils, stable across a wide range of soil conductivity and temperature conditions.
Technical Specifications (Typical):
Applications / Usage Areas:
- • Precision agriculture: monitoring soil moisture for irrigation scheduling, reducing over watering.
- • Soil science and research: measuring soil water content dynamics, calibrating soil moisture sensors.
- • Environmental/hydrology studies: long term soil moisture monitoring, watershed studies.
- • Automated monitoring systems: integration with data loggers/IoT nodes for remote sensing.
User Benefits:
- • Provides accurate, reliable soil moisture readings that are less influenced by soil type, salinity or temperature fluctuations.
- • Enables better decision making in irrigation and water management, potentially saving water and improving crop performance.
- • Digital interface (SDI 12) ensures seamless integration into monitoring systems, enabling data logging and analytics.
- • Durable, field ready design for long term deployment.
Considerations / Best Practice:
- • Ensure proper installation: sensor must have good contact with soil, minimal air gaps, and depth appropriate for measurement objective.
- • Although factory calibrated, soil type extremes (very high clay, high salinity) may require site specific calibration for best accuracy.
- • Data interpretation should consider soil depth, soil structure, crop root zone and other site conditions.
- • Regular checks & maintenance ensure cable integrity, probe condition and correct data logging.


